10 Facts You Didn’t Know About Anthony van Dyck
Anthony van Dyck, a Flemish Baroque painter of remarkable skill, left an indelible mark on art history. His signature style of refined portraits and...
Jimena Aullet 24 October 2024
Rembrandt was a Dutch Golden Age painter during the 17th century. He is known for being one of the greatest artists in art history due to the broad range of media and genres in his paintings. For instance, unlike other Dutch Masters, he painted portraits, self-portraits, landscapes, genre scenes, and even biblical and mythological scenes. Here are 10 of his greatest paintings.

Rembrandt van Rijn, Self Portrait at the Age of 34, 1640, National Gallery, London, UK. Wikimedia Commons (public domain).
Although Rembrandt painted dozens of self-portraits, this is one of his most famous ones, painted at the age of 34. The portrait is well known because of the artist’s clothing. He is wearing expensive materials such as fur, velvet, and a hat covered in jewels. At the time of this painting, Rembrandt was a Dutchman in the 1640s, yet his clothes correspond to a gentleman’s clothing from the 1520s. Simultaneously, he poses himself like Dürer, Raphael, and Titian had during the 16th century. As a result, he portrays himself as a Renaissance man, comparing himself to the great masters.
When the painting was completed, Rembrandt’s clients would easily have recognized his comparison to the Renaissance masters. In doing so, he mimicked a higher social status that artists at the time couldn’t reach, while also emphasizing his equally superb artistic abilities.
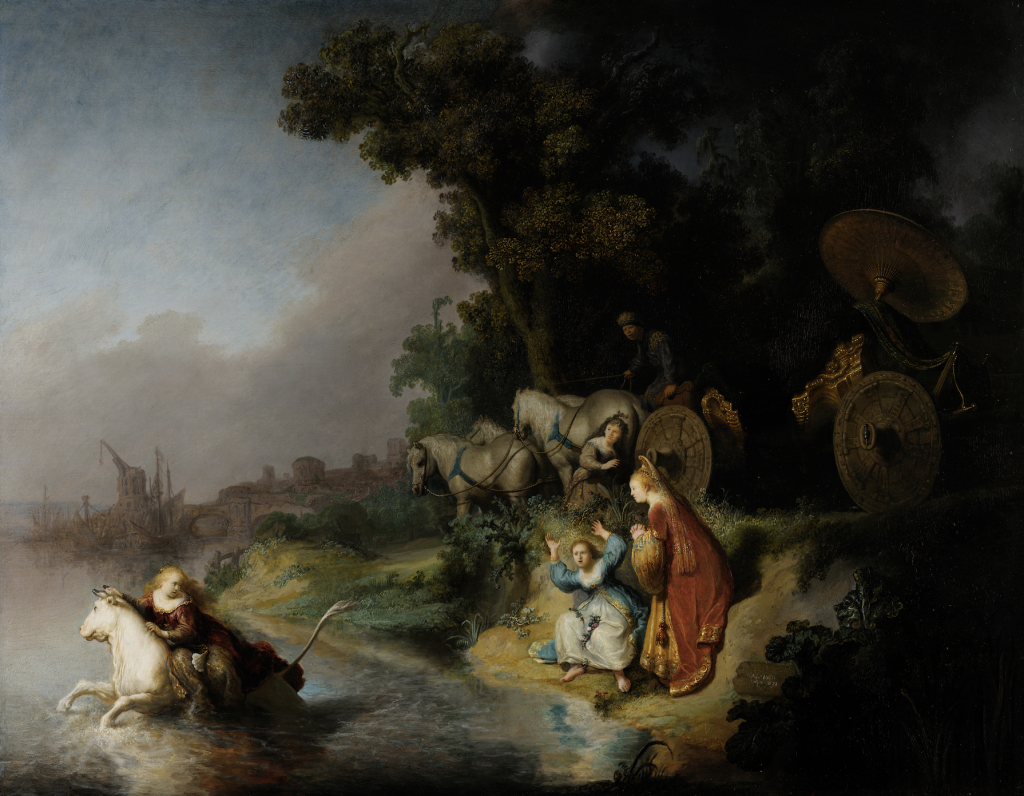

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Abduction of Europa, 1632, J. Paul Getty Museum, California, CA, USA. Wikimedia Commons (public domain).
Continuing Rembrandt’s masterful skill of illustrating numerous subjects is The Abduction of Europa. Even during his long career, mythological subjects were very rare. However, in this dramatic painting Rembrandt paints the story of Princess Europa from Ovid’s Metamorphoses. According to the story, the Roman god Jupiter tried to seduce Europa by disguising himself as a white bull. In the scene, Rembrandt paints the moment that Jupiter carries Europa across the sea, away from her home and friends, to a distant land.
Europa and her friends look distraught. Rembrandt even included a visual illusion of Amsterdam in this painting; behind the grey mist in the background, one can see a city, which could either be an allusion to the ancient town of Tyre or contemporary Amsterdam. Regardless, Rembrandt captured the moment in exquisite detail through the visual effects of color. As sunlight shines from the left of the composition onto the water, darkness remains behind the trees.

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Storm on the Sea of Galilee, 1633, Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum, Boston, MA, USA. Wikimedia Commons (public domain).
Perhaps the most intriguing painting is Christ in the Storm on the Sea of Galilee, not only because it is Rembrandt’s only known seascape ever painted, but also because it was stolen in 1990 from the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston, Massachusetts. The painting expresses Rembrandt’s earlier style of painting when he first moved to Amsterdam from his hometown of Leiden.
In this biblical scene, we see a ravenous storm rocking a boat in the sea. The boat is full of scared disciples, while Christ is shown as the only person remaining calm during the storm. According to the museum, “The painting showcases the young Rembrandt’s ability not only to represent a sacred history but also to seize our attention and immerse us in an unfolding pictorial drama.” Furthermore, his use of dramatic light attracts our attention to the painting. Unfortunately, the painting remains missing to this day.
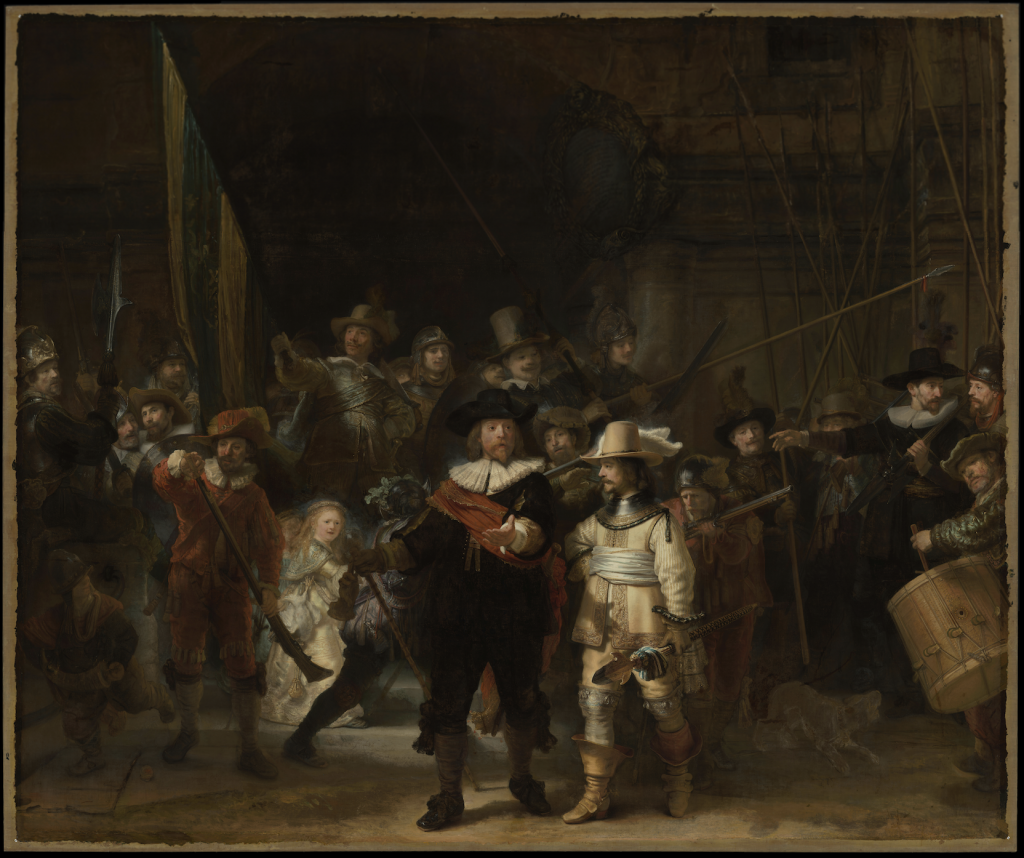

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Night Watch, 1642, Amsterdam Museum, on permanent loan to the Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Rembrandt’s most famous painting, The Night Watch, earned him success during his lifetime. It was commissioned for one of the three headquarters of Amsterdam’s civic guard. It is famous due to its sheer size (the figures are almost life-size), tenebrism (dramatic use of light), and composition. Through his use of light, viewers become focused on the three main characters in the painting. At first, you are drawn to the composition’s two soldiers, front and center. To their right the third figure glows, it is a woman holding a chicken.
The painting is filled with motifs that symbolize a militia and war; Rembrandt even uses the color yellow on the clothing of two of the three main characters to represent victory.

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Jewish Bride, 1665-1669, Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam, Netherlands. Wikimedia Commons (public domain).
Commonly known as The Jewish Bride, the painting’s original title was Portrait of a Couple as Isaac and Rebecca. The Jewish Bride was given its nickname by an Amsterdam art collector in the 19th century when he believed the sitter to be a Jewish father presenting a necklace to his daughter on her wedding day. Over the years there has been considerable debate over the sitter’s identities. The most common identification of the figures is the Biblical couple of Isaac and Rebecca.
Regardless of the debates, the work was done during the later part of Rembrandt’s career with masterful skill. This is recognized through Rembrandt’s characteristic rich earth tones and thin versus thick (impasto) strokes of paint.

Rembrandt van Rijn, Saskia van Uylenburgh as Flora, State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia.
As a tribute to his wife, Saskia van Uylenburgh, Rembrandt painted her as Flora, the goddess of spring and flowers. This beautiful mythological painting showcases the artist’s skill of mastering any subject. Flora stands in a grotto, dressed in elegant silk textiles and satin embroidered with silver thread. Rembrandt might have been inspired by Renaissance artist Titan and his paintings of Flora.
The adoration of his wife echoes through this life-size, quarter-length portrait. Rembrandt painted it in 1634, the same year as their marriage, a joyful time in his life. The artist would continue to paint his wife on three separate occasions.
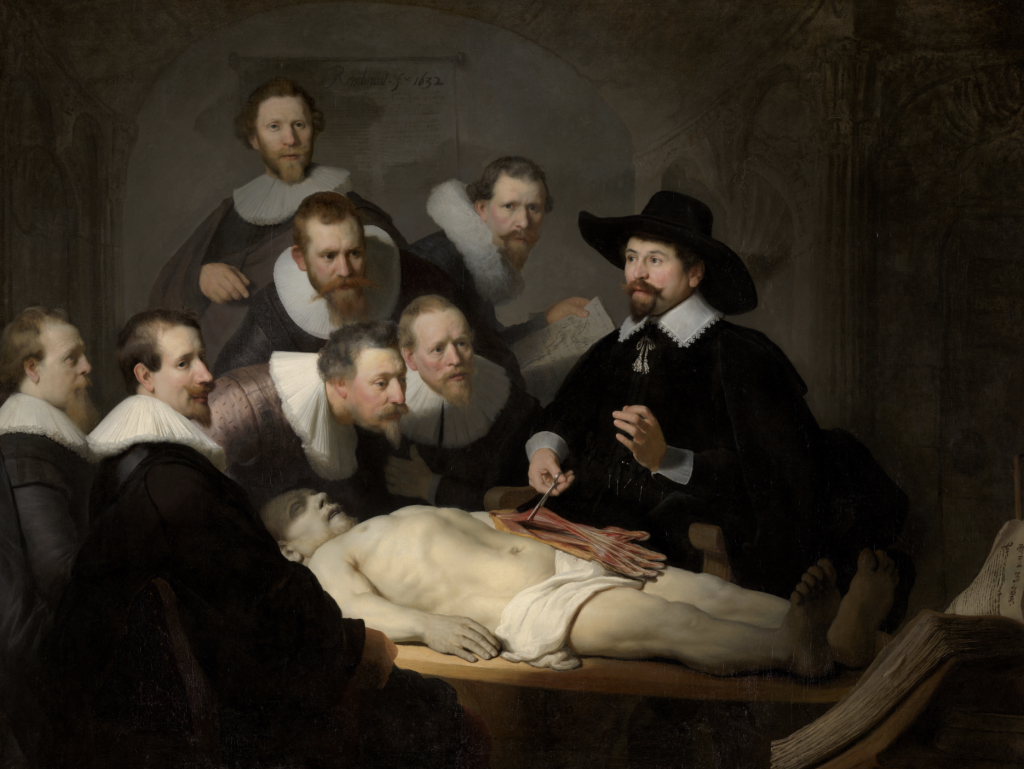
Rembrandt van Rijn, The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp, 1632, Mauritshuis, The Hague, Netherlands.
Next is Rembrandt’s painting for the Surgeons Guild, The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp. Regarded as one of Rembrandt’s early masterpieces, it shows Nicolaes Tulp explaining the arm muscles to a group of doctors. A few doctors pictured in the painting paid a commission to be featured.
During the 17th century, anatomy lessons were a social event that only occurred once a year to the public. Due to this rule, the Surgeon’s Guild commissioned a painting every few years by a leading portraitist to capture the moment in science. As a result, this became Rembrandt’s first major commission in Amsterdam. Again, we recognize Rembrandt’s signature style of tenebrism through the dramatic effect of light and shadows on the doctor’s faces.
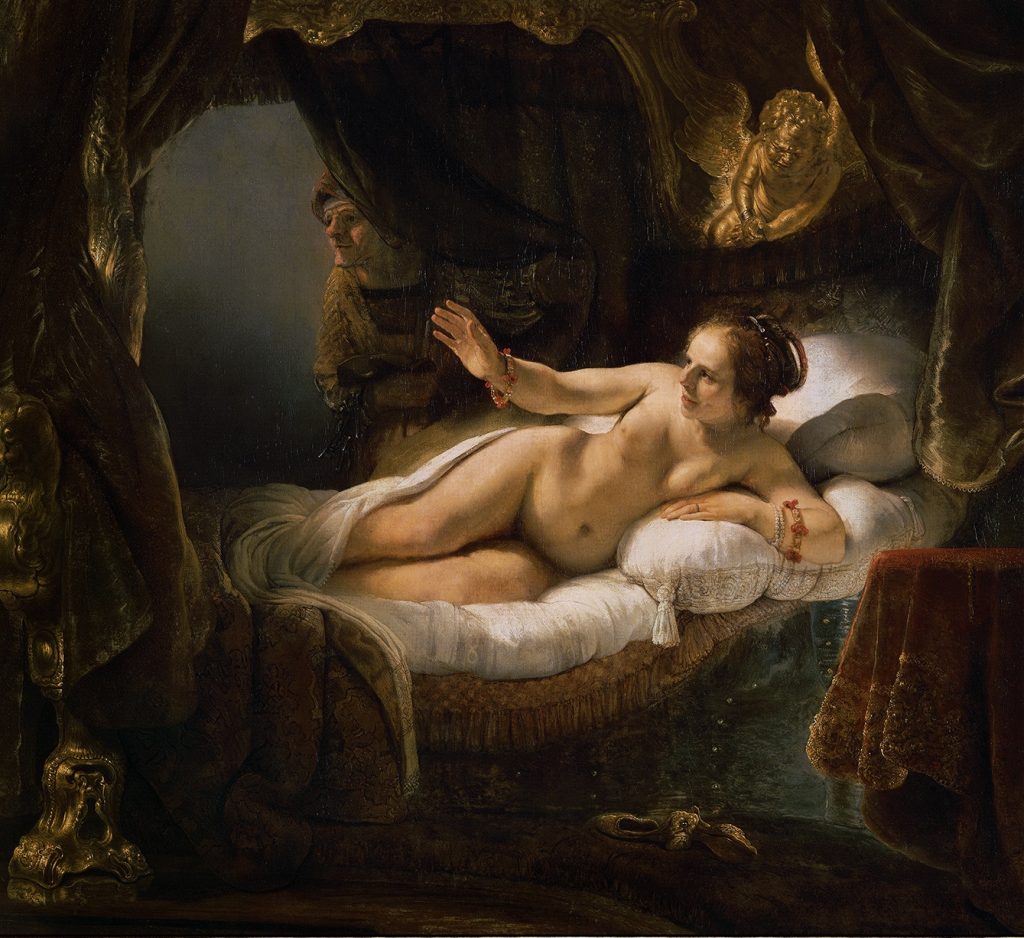

Rembrandt van Rijn, Danaë, 1636, Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia.
Continuing his trend of life-sized figures, Rembrandt paints a character from Greek mythology. Danaë, the mother of Perseus, is shown welcoming Zeus, who has just impregnated her by appearing as a shower of gold. While the original painting of Danaë was created in 1636, Rembrandt returned to it later in the 1640s.
This gloriously detailed painting might have been Rembrandt’s most treasured work. Perhaps that is why he returned to rework major details of the figure’s body, such as her head, arms, and legs. The painting has been part of the Hermitage Museum’s collection since the 18th century and was vandalized in 1985 but was restored immediately after.

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Return of the Prodigal Son, 1661–1669, Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia.
One of the last works created by Rembrandt is The Return of the Prodigal Son, painted in 1669. The Biblical narrative depicts the prodigal son returning to his father after losing his inheritance. According to the parable, the son returns to his father, begging for forgiveness, and asks to be a servant. The father forgives him and receives him back into the family regardless of the fortune he has lost. Rembrandt’s painting highlights the scene by illuminating the father and son’s interaction.
Rembrandt felt very connected to this parable and sketched numerous depictions of its theme.

Rembrandt van Rijn, The Slaughtered Ox, 1655, Louvre Museum, Paris, France.
Finally, Rembrandt painted The Slaughtered Ox in 1655. As the only still-life painting mentioned in this list, it is quite gruesome in its imagery. However, it follows the tradition of artists capturing butchery. Rembrandt creates a heavy focus on perfecting the colors of the slayed ox and provides texture to the painting through his use of impasto. Again, he utilizes his skill of tenebrism through light and a cast shadow, which shifts the viewer’s attention to a woman opening a door in the background. At this moment, the painting is no longer a still life but instead a genre painting. While many believe this imagery is a reference to the Prodigal Son (a parable near and dear to Rembrandt), it might simply be a reference to butchery. Or perhaps it provided Rembrandt the opportunity to showcase another one of his magnificent skills as a painter.
DailyArt Magazine needs your support. Every contribution, however big or small, is very valuable for our future. Thanks to it, we will be able to sustain and grow the Magazine. Thank you for your help!